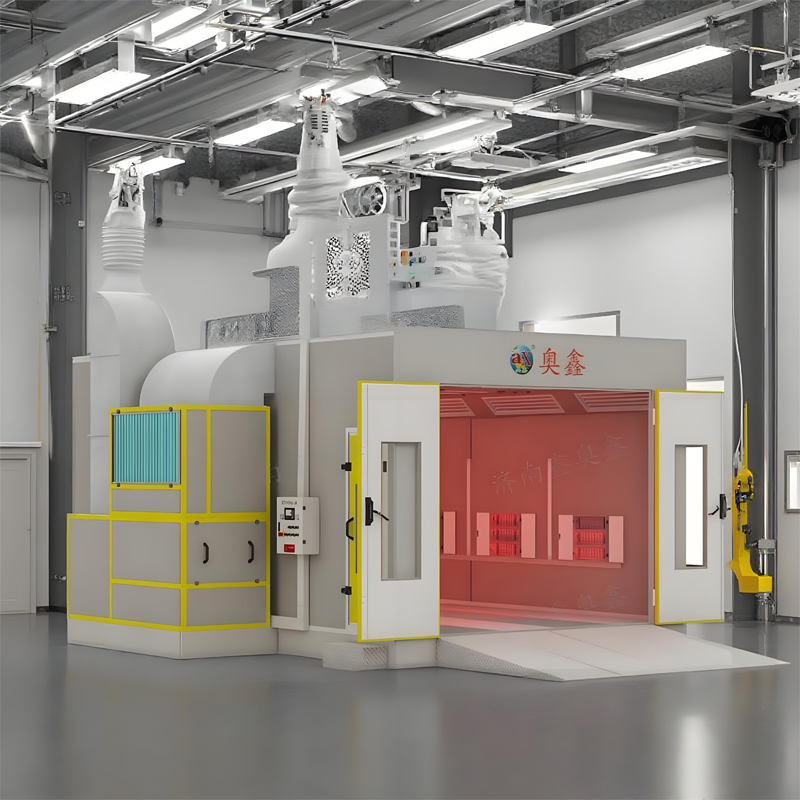
Modern industrial facilities rely heavily on advanced spray booth systems to ensure safe and efficient coating operations. These specialized enclosures have evolved significantly from their basic predecessors, incorporating cutting-edge safety technologies and design principles that protect workers, equipment, and the environment. Understanding the comprehensive safety features of contemporary spray booth installations is crucial for facility managers, safety professionals, and industrial coating specialists who prioritize operational excellence and regulatory compliance.
Fire Prevention and Suppression Systems
Advanced Fire Detection Technology
Contemporary spray booth designs integrate sophisticated fire detection systems that utilize multiple sensing technologies to identify potential ignition sources before they develop into dangerous situations. These systems typically employ flame detectors, heat sensors, and smoke detection devices strategically positioned throughout the booth structure. The multi-layered approach ensures rapid response times and minimizes false alarms that could disrupt production schedules unnecessarily.
Infrared flame detectors represent a significant advancement in spray booth fire safety, capable of detecting hydrocarbon fires within milliseconds of ignition. These sensors monitor specific wavelengths associated with combustion processes and can distinguish between actual fires and other heat sources like welding operations or hot work activities. The integration of these advanced detection systems with automated shutdown procedures creates a comprehensive safety net that protects both personnel and valuable equipment investments.
Automated Suppression Mechanisms
Modern spray booth installations feature state-of-the-art suppression systems designed specifically for coating operations involving flammable materials. Water-based sprinkler systems remain common, but many facilities now utilize specialized suppression agents like foam or inert gas systems that provide superior fire control without causing secondary damage to sensitive equipment or finished products.
The activation of suppression systems triggers immediate safety protocols including automatic shutdown of spray equipment, closure of isolation dampers, and activation of emergency ventilation modes. These coordinated responses ensure that fire suppression efforts are maximally effective while preventing the spread of flames or toxic gases to adjacent work areas. Regular testing and maintenance of these systems ensures reliable operation when emergency situations arise.
Ventilation and Air Quality Management
Explosion-Proof Ventilation Systems
Proper ventilation design represents perhaps the most critical safety element in any spray booth configuration. Modern systems utilize explosion-proof fans and motors that eliminate potential ignition sources while maintaining the airflow rates necessary for safe coating operations. These specialized components are constructed with non-sparking materials and incorporate design features that prevent the accumulation of static electricity during operation.
Air change rates in contemporary spray booth designs typically exceed industry minimum requirements, often providing complete air replacement every 60 to 90 seconds. This aggressive ventilation approach ensures that solvent vapors and overspray particles are continuously removed from the work environment, maintaining concentrations well below lower explosive limits and occupational exposure thresholds.
Filtration and Emission Control
Advanced filtration systems in modern spray booth installations serve dual purposes of worker protection and environmental compliance. Primary filtration stages capture overspray particles and larger contaminants, while secondary stages utilize high-efficiency particulate air filters or activated carbon systems to remove fine particles and volatile organic compounds before air discharge.
Many facilities now incorporate real-time air quality monitoring systems that continuously assess both particulate and vapor concentrations within the spray booth environment. These monitoring systems provide immediate feedback to operators and can trigger automatic adjustments to ventilation rates or coating process parameters when contamination levels approach predetermined safety thresholds.
Electrical Safety and Grounding Systems
Intrinsically Safe Electrical Components
Electrical safety in spray booth environments requires specialized components rated for hazardous locations where flammable vapors may be present. All electrical equipment within the booth structure must meet strict classification requirements, typically Class I, Division 1 or Division 2 specifications depending on the specific location and vapor concentration potential.
Lighting systems utilize explosion-proof fixtures with specialized lens materials that prevent sparking even if damaged during operations. Control panels and switches are housed in purged enclosures that maintain positive pressure with clean air, preventing the ingress of flammable vapors that could create ignition hazards. These safety measures ensure that electrical systems can operate reliably without contributing to fire or explosion risks.
Comprehensive Grounding Networks
Static electricity generation during spray coating operations presents significant safety hazards that modern spray booth designs address through comprehensive grounding and bonding systems. All metallic components within the booth structure are interconnected through low-resistance pathways that safely dissipate static charges to ground potential.
Spray equipment, including guns, hoses, and fluid delivery systems, incorporate conductive elements that maintain electrical continuity throughout the coating process. Regular testing and maintenance of grounding systems ensures continued effectiveness, with many facilities implementing automated monitoring systems that provide continuous verification of grounding integrity.
Personnel Safety and Emergency Response
Emergency Shutdown Systems
Modern spray booth installations incorporate multiple emergency shutdown mechanisms that allow immediate cessation of all coating operations in response to safety concerns. Emergency stop buttons are strategically located both inside and outside the booth structure, providing accessible shutdown capability from various positions around the work area.
These shutdown systems typically interrupt power to spray equipment, close material supply valves, and activate emergency ventilation modes simultaneously. The coordinated response ensures that potential hazards are minimized quickly while maintaining safe conditions for personnel evacuation if necessary. Visual and audible alarm systems provide clear indication of emergency conditions to all personnel in the vicinity.
Personal Protective Equipment Integration
Contemporary spray booth designs consider the integration of personal protective equipment as an essential safety element rather than an afterthought. Supplied air systems provide clean breathing air to operators working within the booth environment, eliminating exposure to coating materials and ensuring adequate oxygen supply during extended work periods.
Communication systems allow continuous contact between booth operators and external supervisors, providing an additional safety layer that enables rapid response to emergency situations or equipment malfunctions. These systems are designed to function reliably in the challenging environment of active coating operations, with noise-canceling features that ensure clear communication despite high ambient sound levels.
FAQ
How often should spray booth safety systems be inspected and maintained
Safety systems in spray booth installations require regular inspection and maintenance according to manufacturer specifications and regulatory requirements. Fire detection and suppression systems typically need monthly visual inspections and annual comprehensive testing by qualified technicians. Ventilation systems should be inspected quarterly with filter replacements as needed based on usage intensity. Electrical grounding systems require annual continuity testing to ensure proper functionality.
What training requirements apply to spray booth operators
Operators working in spray booth environments must receive comprehensive training covering safety procedures, emergency response protocols, and proper use of personal protective equipment. Training programs should address hazard recognition, fire prevention principles, and proper handling of coating materials. Regular refresher training ensures that operators maintain current knowledge of safety procedures and any updates to equipment or processes.
How do modern spray booths address environmental compliance requirements
Contemporary spray booth designs incorporate advanced emission control technologies that help facilities meet stringent environmental regulations. High-efficiency filtration systems capture overspray particles and volatile organic compounds before air discharge. Many installations include thermal oxidizers or other destruction devices that eliminate harmful emissions. Continuous monitoring systems provide documentation of emission levels for regulatory reporting requirements.
What factors influence the selection of suppression systems for spray booth applications
Selection of fire suppression systems depends on several factors including the types of coating materials used, booth size and configuration, and proximity to sensitive equipment or finished products. Water-based systems are cost-effective but may cause secondary damage. Foam systems provide excellent fire control for flammable liquid fires. Inert gas systems offer clean suppression without residue but require careful consideration of personnel safety during discharge.

